Yo, folks! As a supplier of Medical X-ray Machine, I've been getting a bunch of questions about how accurate these machines are when it comes to diagnosing diseases. So, I thought I'd sit down and write this blog to clear things up.
Let's start with the basics. X-ray machines work by sending a small amount of radiation through your body. Different tissues in your body absorb this radiation in varying degrees. For example, bones are dense and absorb a lot of the X-ray, which makes them appear white on the X-ray image. Soft tissues like muscles and organs absorb less, showing up as shades of gray, and air in your lungs absorbs very little, so it looks black.
Now, when it comes to accuracy, X-ray machines are pretty darn good at what they do, especially for certain things. Take bone fractures, for instance. Orthopedic X-ray Machine are specifically designed to get clear images of bones. They can spot a broken bone with high precision. A simple X-ray can show the location, type, and severity of a fracture. This is super important for doctors to decide on the right treatment, whether it's a cast, surgery, or just some rest.
But it's not all sunshine and rainbows. X-rays have their limitations. They're not as great at diagnosing soft tissue problems. For example, if you have a ligament tear in your knee, an X-ray might not show it clearly. Ligaments are made of soft tissue, and they don't show up well on a regular X-ray. That's where other imaging techniques like MRI or ultrasound come in. They can provide more detailed images of soft tissues.
Another area where X-rays might fall short is in detecting early-stage diseases. Some diseases, like certain types of cancer, may not show up on an X-ray until they've progressed to a certain stage. This is because in the early stages, the changes in the tissue might be too small to be visible on an X-ray. So, while X-rays can be a useful tool for screening, they're not always enough on their own for an early and accurate diagnosis.
When it comes to X-ray of Extremities, they're pretty accurate for things like joint problems. X-rays can show signs of arthritis, such as joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and changes in the bone structure. This helps doctors understand the extent of the disease and plan the appropriate treatment. But again, for more detailed information about the soft tissues around the joints, other imaging methods might be needed.
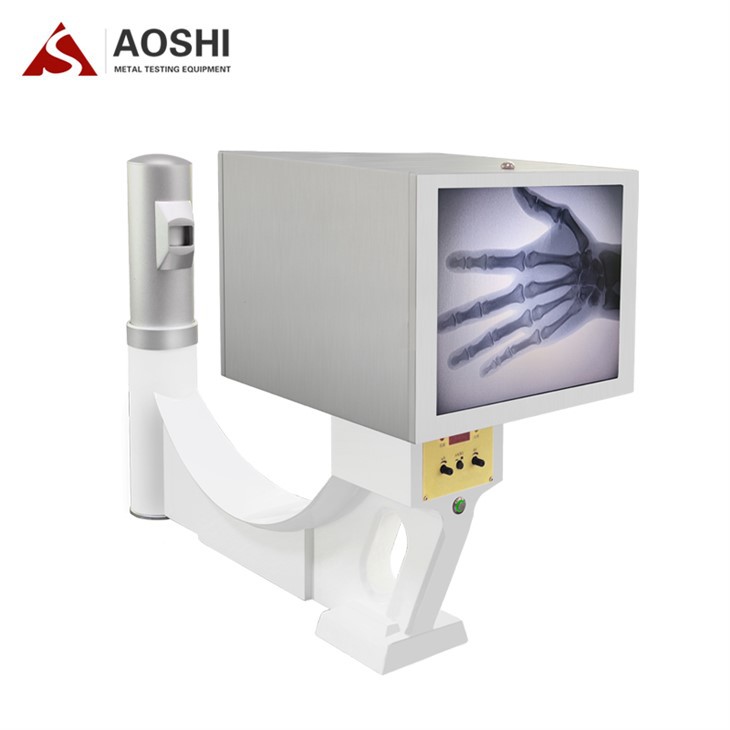

The accuracy of an X-ray also depends on a few other factors. The quality of the machine itself is crucial. A high - quality Medical X-ray Machine will produce clearer images, which means a better chance of accurate diagnosis. The skill of the technician taking the X-ray is also important. If the X-ray is taken at the wrong angle or with the wrong settings, it can lead to a less accurate image. And finally, the experience of the doctor interpreting the X-ray matters a lot. A seasoned radiologist will be better at spotting subtle signs and making an accurate diagnosis.
So, in conclusion, X-ray machines are a valuable tool in the medical field. They're great for diagnosing bone fractures, joint problems, and some other conditions. But they're not perfect. They have limitations when it comes to soft tissue and early - stage disease detection. However, when used in combination with other imaging techniques and the expertise of medical professionals, they can play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases accurately.
If you're in the market for a Medical X-ray Machine, Orthopedic X-ray Machine, or need an X-ray of Extremities, I'd love to talk to you. We offer high - quality machines that can provide accurate and clear images. Whether you're a small clinic or a large hospital, we have the right solution for you. Reach out to us to start a discussion about your needs and how we can help you with your medical imaging requirements.
References
- Bushberg, J. T., Seibert, J. A., Leidholdt, E. M., & Boone, J. M. (2012). The essential physics of medical imaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Bontrager, K. L., & Lampignano, J. P. (2019). Textbook of radiographic positioning and related anatomy. Elsevier Health Sciences.
